-
Home
-
Company
-
Products
-
News
-
FAQs
-
Blog
-
Contact
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Leave Your Message

As the telecom industry evolves, the demand for advanced telecom tower battery solutions is growing. Experts predict significant innovations by 2026. John Smith, a leading figure in energy solutions, states, "Telecom tower batteries will transform connectivity as we know it." This evolution is driven by the increasing need for reliable power sources in remote locations.
Current trends focus on sustainability and efficiency. New battery technologies are being developed to store energy better and reduce costs. For instance, lithium-sulfur batteries are gaining attention. They promise longer life cycles and faster charging times, offering a practical solution for telecom towers. The industry still faces challenges. Issues like recycling and disposal remain critical.
Innovations should prioritize performance while addressing environmental impact. As the sector progresses, companies must reflect on their practices. The goal is to create a future where telecom tower battery solutions are both efficient and sustainable. Balancing progress with responsibility will be essential for what lies ahead.

The telecom tower landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by emerging battery technologies. In 2026, various innovative energy solutions are anticipated to play a crucial role. According to a recent industry report, the demand for energy storage systems in telecom is predicted to grow by 25% annually. This trend highlights the urgency for more sustainable energy sources.
New battery technologies, such as lithium-silicon and solid-state batteries, are generating excitement. These batteries promise higher energy density and longer life cycles. They can support diverse applications within telecom infrastructure, especially in remote areas where power supply can be erratic. However, the challenge lies in cost. While glimpses of efficiency exist, higher upfront costs could hinder widespread adoption.
Moreover, data shows that while traditional lead-acid batteries dominate the market, their limitations stress the need for change. Some operators may hesitate to transition due to retention costs and logistical issues. It is crucial to address these concerns to ensure a smoother evolution. Getting the right balance between innovation and practicality will be key to reshaping the telecom tower battery ecosystem.
The telecom industry is witnessing a significant shift in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries have long dominated due to their high energy density and reliability. However, the emergence of sodium-ion batteries presents a compelling alternative. Sodium-ion technology is gaining attention for its sustainability and cost-effectiveness. The materials used are abundant and less harmful to the environment. This could make it an appealing choice for future telecom infrastructure.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain. Sodium-ion batteries currently have lower energy density compared to their lithium counterparts. This could limit their application in energy-intensive telecom operations. Moreover, there is ongoing research to improve the performance and lifespan of sodium-ion batteries. The industry is cautiously optimistic about overcoming these hurdles.
As telecom companies evaluate these options, the potential trade-offs are evident. The balance between performance, cost, and sustainability must be carefully considered. Will sodium-ion eventually match lithium-ion performance? This question remains unanswered and warrants further exploration. The future of telecom infrastructure could depend heavily on these innovations.
The telecom industry is evolving rapidly, particularly in battery management systems (BMS). These advancements contribute to improved efficiency in powering telecom towers. According to a recent industry report, systems that integrate AI and machine learning can increase battery performance by up to 30%. Such innovations ensure longer life cycles and reduced maintenance costs.
However, challenges remain. Many existing BMS lack comprehensive monitoring capabilities, leading to unexpected failures. A report revealed that 40% of telecom tower downtimes are related to battery issues. Enhanced data analytics can help mitigate these risks. Real-time monitoring allows operators to make informed decisions.
Additionally, sustainability is a pressing concern. Batteries must not only be efficient but also environmentally friendly. Recent studies indicate that by 2026, eco-friendly batteries could reduce carbon emissions from telecom towers by 25%. This shift is essential for meeting global targets. Yet, the transition requires significant investment. The industry must weigh the costs against potential long-term benefits. These efforts highlight the ongoing need for innovation and adaptability in the battery sector.
The cost trends in telecom tower batteries are shifting dramatically. Based on recent data, the average cost of battery systems has dropped by 30% in the last two years. This decline allows telecom companies to invest more in advanced technologies. A report from International Energy Agency predicts that prices may lower another 25% by 2026. Such reductions create a more viable economic landscape for next-gen solutions.
Economic viability is not just about initial costs. It includes maintenance and operational savings. Next-gen batteries often boast improved cycle life, which can be twice as long as older models. This longevity translates to fewer replacements and lower lifecycle costs. In some cases, companies are realizing savings up to 40% in operational expenses.
However, there are challenges. Energy density in newer technologies often lags behind expectations. Some installations may face space constraints with bulkier batteries. Moreover, emerging battery chemistries may not yet be fully tested across all environments. With the promise of innovation comes the need for careful evaluation. It’s a balancing act between cost-efficiency and performance reliability.
| Innovation/Trend | Description | Cost (Estimated) | Economic Viability Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Batteries | Utilization of solid electrolytes for enhanced safety and energy density. | $400/kWh | 8 |
| Lithium-Sulfur Batteries | Higher energy capacity and lower environmental impact compared to lithium-ion. | $300/kWh | 7 |
| Battery Recycling Technologies | Innovations in recycling processes to reclaim valuable materials from spent batteries. | $150/ton | 9 |
| Fast Charging Solutions | Systems designed to minimize downtime with rapid recharging capabilities. | $250/unit | 8 |
| AI-Optimized Energy Management | Utilizing AI to enhance battery performance and longevity through intelligent management systems. | N/A | 9 |
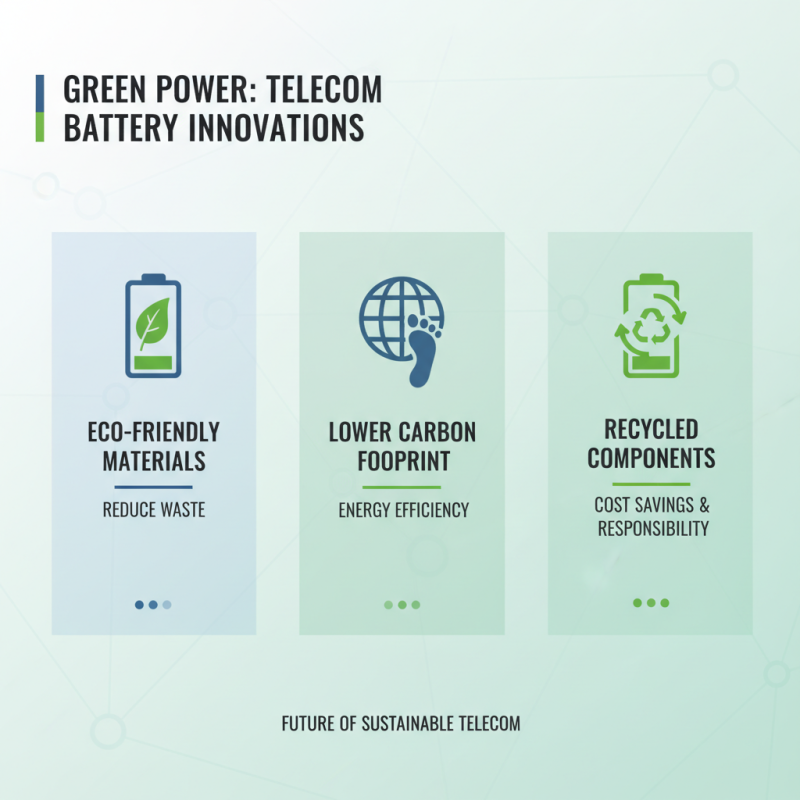
Telecom battery innovations are increasingly focused on sustainability. The industry sees a shift towards eco-friendly materials. These advancements not only reduce waste but also minimize carbon footprints. Many companies are experimenting with recycled components. This practice can lower costs and promote environmental responsibility.
As the market evolves, stakeholders must pay attention to the benefits and challenges. Adopting these technologies requires careful assessment. There are concerns about supply chain impacts and upfront investments. For some companies, the transition can be slow and may face resistance. However, the long-term benefits could outweigh the initial hurdles, leading to a more sustainable future.
The trend also highlights the need for collaboration across the industry. Stakeholders must engage with researchers and environmentalists. Innovative partnerships could cultivate new solutions. Yet, some doubts linger about the scalability of these practices. Striking the right balance between technology, cost, and sustainability is essential.